Oxygen therapy is a critical medical intervention that helps individuals who struggle to obtain adequate oxygen on their own. Whether due to acute conditions like COVID-19 or chronic illnesses such as COPD and emphysema, oxygen therapy ensures your body receives the oxygen it needs to function optimally. In essence, this therapy can dramatically improve your quality of life by stabilising blood oxygen levels and preventing organ damage.
If you are exploring the basics of oxygen therapy for the first time, it’s essential to understand how it works and its impact on your health. Oxygen therapy involves administering oxygen either in liquid or gas form, depending on specific needs. Devices used include nasal cannulas, oxygen masks, and portable oxygen concentrators. These tools help maintain healthy oxygen saturation levels, typically above 95%.
With a trusted reputation for high-quality, reliable equipment, Ramdon.com offers everything from standard oxygen tanks to the latest portable units, ensuring you get the best care possible. Their expertise in oxygen therapy can help you make informed decisions about your health needs.
Fundamentals of Oxygen Therapy
Oxygen therapy is a critical intervention in modern healthcare used to manage a variety of respiratory conditions. It involves the administration of supplemental oxygen to maintain adequate oxygen levels in the blood, ensuring tissues and organs receive the oxygen they need.
Understanding Oxygen Therapy and Its Purposes
Oxygen therapy has several purposes, including treating acute and chronic hypoxemia, reducing the workload of the heart and lungs, and improving the quality of life for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma. By maintaining appropriate oxygen saturation levels, oxygen therapy helps prevent complications associated with low oxygen levels, such as organ failure and respiratory distress.
Key benefits:
- Correcting Hypoxemia: Supports patients with dangerously low blood oxygen levels.
- Reducing Symptoms: Alleviates breathlessness and other symptoms in chronic conditions.
- Enhancing Organ Function: Ensures organs receive sufficient oxygen to function correctly.
Ramdon.com offers a variety of oxygen therapy products tailored to meet individual needs, providing reliable solutions for both home and hospital settings.
Types of Oxygen Delivery Systems
Various oxygen delivery systems are used based on the patient’s condition, required flow rate, and setting (home or hospital).
Common systems:
- Nasal Cannula: Delivers low to moderate oxygen concentrations and is suitable for long-term therapy. It is comfortable and allows patients to speak and eat.
- Face Mask: This is used for higher oxygen concentrations. It covers the nose and mouth and is often seen in emergency and acute care settings.
- Oxygen Concentrator: This device extracts oxygen from ambient air to provide a continuous oxygen supply. It is economical and portable for home use.
- Ventilators: Essential for patients with severe respiratory distress who require mechanical assistance to breathe.
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) and BiPAP: Devices commonly used for sleep apnoea and other conditions requiring airway support during sleep.
The choice of an oxygen delivery system is guided by the patient’s specific medical needs and the prescription provided by a healthcare provider.
Ramdon.com offers expert advice and a wide range of oxygen equipment to ensure you receive the most suitable and high-quality solutions for your oxygen therapy needs.
Clinical Considerations and Safety
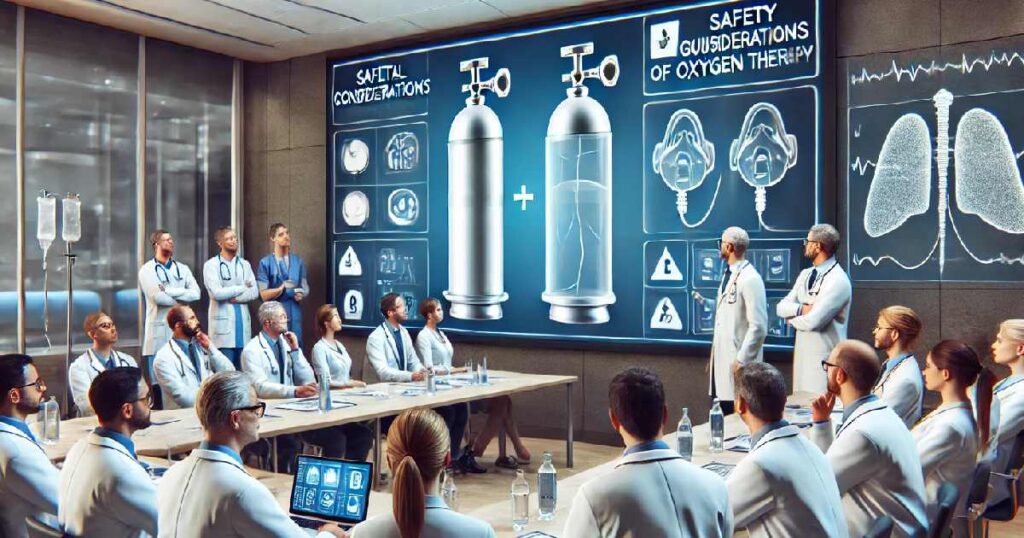

Understanding the basics of oxygen therapy involves recognising its clinical considerations and ensuring its safe administration. You must be aware of potential complications, individual patient needs, and vigilant monitoring to guarantee efficacy and safety.
Managing Risks and Recognising Complications
Oxygen therapy, while life-saving, is not without risks. Hypoxia and hyperoxia are critical to monitor. High concentrations can lead to oxygen toxicity and potentially severe complications such as lung damage and reduced carbon dioxide levels.
Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) or Pulmonary Fibrosis may exhibit fluctuating oxygenation status. Pulse oximetry and arterial blood gas analyses are essential to monitor oxygenation and carbon dioxide levels.
Complications can include tachypnea, dyspnea, and cyanosis. Watch for signs like increased respiratory rate and blue-tinged skin, which may necessitate interventions like intubation.
Patient-Centric Care
Oxygen therapy must be tailored to individual patient needs. Patients with Cystic Fibrosis or Sleep Apnea require specialised approaches. Use tools like spirometry to assess lung function and adjust therapy accordingly.
Ensure continuous monitoring of oxygen levels, especially in chronic lung conditions. Address concerns related to anaemia or accompanying medications that may interfere with therapy.
Variations across the lifespan must be considered. Infants and elderly patients may require different oxygen levels and delivery methods. Document actions and observations meticulously and adjust for any deviations from norms.
Safe Administration and Monitoring
Safety is paramount in oxygen therapy. Use devices like the simple face mask or portable oxygen tanks as prescribed, ensuring correct flow rates and delivery systems. Monitor blood vessels and systemic arteries for adequate oxygenation.
Combustion risks must be mitigated. Avoid open flames near oxygen sources and educate patients on safe use. Human life depends on strict adherence to safety protocols to prevent smoke inhalation and potential complications.
Our expertise ensures the right equipment and guidance for safe and effective use, fostering positive patient outcomes. Pulse oximetry and continuous monitoring are vital tools in maintaining the right oxygen levels during therapy. Always integrate safety precautions into your routine to prevent adverse events.
Frequently Asked Questions
Accessing oxygen therapy solutions can significantly improve your quality of life. Here, we answer common questions about different types of oxygen therapy, safe administration methods, and key benefits.
What are the different types of oxygen therapy available?
There are several types of oxygen therapy, including:
- Compressed gas systems: These involve oxygen cylinders that store oxygen under pressure.
- Liquid oxygen systems: Oxygen is stored as a very cold liquid in a vessel and converted to gas as used.
- Oxygen concentrators: These devices concentrate oxygen from the surrounding air for patient use.
What are the potential disadvantages associated with oxygen therapy?
While oxygen therapy can be life-saving, it comes with potential drawbacks:
- Dependency: Prolonged use can lead to reliance on the device.
- Mobility issues: Carrying cylinders or concentrators can restrict movement.
- Nasal dryness or irritation: Continuous use might cause discomfort in the nasal passages.
How can oxygen therapy be administered safely at home?
Safe administration of oxygen therapy at home involves several steps:
- Keep away from flames: Ensure oxygen tanks are at least 8-10 feet from open flames or sparks.
- Proper storage: Secure tanks to prevent them from falling.
- Regular maintenance: Clean tubing with a damp cloth and replace it as necessary. Check and clean the concentrator filters and alarm weekly.
Ramdon.com offers a range of safe and reliable oxygen therapy products for home use.
What are the primary benefits one can receive from undergoing oxygen therapy?
Undergoing oxygen therapy provides several benefits:
- Improved oxygen levels: Helps maintain healthy blood oxygen levels, particularly in people with COPD, emphysema, or other respiratory conditions.
- Better sleep and mental clarity: Good oxygen levels can enhance sleep quality and cognitive function.
- Enhanced physical activity: Oxygen therapy can reduce fatigue and improve exercise tolerance.
What guidelines should be followed when determining the dosage of oxygen for a patient?
Determining the correct dosage involves:
- Assessing oxygen levels: Using pulse oximetry to measure blood oxygen saturation (SaO2).
- Medical prescription: Following the specific litre flow rate prescribed by a healthcare provider.
- Regular monitoring: Continuously checking oxygen levels to adjust the dosage as necessary.
What are the purpose and underlying principles of administering oxygen therapy?
Oxygen therapy aims to:
- Correct hypoxemia: Address low blood oxygen levels by providing additional oxygen.
- Reduce cardiopulmonary workload: Ease the strain on the heart and lungs.
- Support organ function: Ensure vital organs receive adequate oxygen to function properly.
Understanding the basics of oxygen therapy helps you manage and benefit from the treatment effectively. Visit Ramdon.com for expert advice and top-tier oxygen therapy products.


