Plants harness sunlight’s energy through a remarkable process called photosynthesis. At its heart, this involves converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, the latter being a crucial by-product. Photosynthesis is not only essential for the creation of oxygen but also supports life on Earth by maintaining the balance of gases in the atmosphere. If you’re wondering how oxygen facilitates photosynthesis in plants, this article is the right one for you.
The role of oxygen in photosynthesis is multifaceted. Chlorophyll, the pigment in plants responsible for capturing light energy, initiates a series of reactions that ultimately split water molecules, releasing oxygen. Oxygen is then released into the atmosphere, sustaining various life forms. This facilitates not just plant biology but also the overarching ecosystem.
Ramdon supports agricultural industries by leveraging the knowledge of how photosynthesis operates, enhancing plant growth and productivity. Understanding the role of oxygen in this process can lead to innovative methods to increase crop yield and efficiency, benefiting both the environment and the economy. By improving the fundamental processes of photosynthesis, you ensure healthier plants and a more robust agricultural sector.
The Process of Photosynthesis
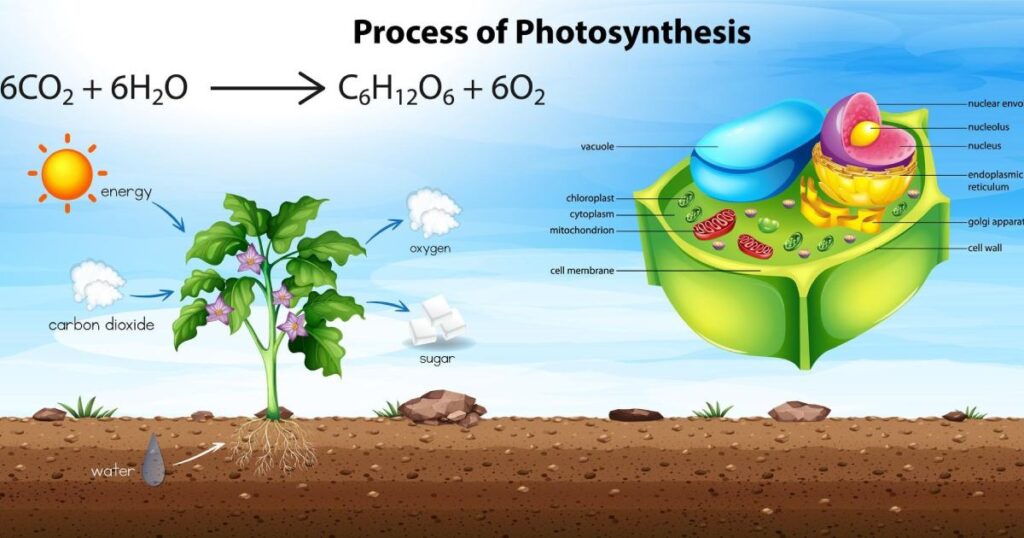
Photosynthesis is a complex process carried out by plants, algae, and some bacteria. It converts light energy into chemical energy. Moreover, the stages include capturing light energy, converting it into sugars, and the integral role of oxygen in facilitating the entire process.
Capturing Light Energy
Plants capture light energy using pigments such as chlorophyll located within the chloroplasts. The process begins when photons from sunlight hit the thylakoid membranes, initiating light-dependent reactions.
In these reactions, photosystem II absorbs light energy, exciting electrons to a higher energy state. This triggers the decomposition of water molecules, releasing oxygen into the atmosphere.
Converting Energy into Sugars
Excited electrons travel through the electron transport chain, forming ATP and NADPH. These molecules store the chemical energy required for the next stage, the Calvin cycle.
During the Calvin cycle, carbon dioxide is fixed into organic molecules. Through a series of steps involving enzymes, carbon fixation results in the formation of 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA). Subsequently, these molecules are transformed into G3P, which can be used to synthesise glucose and other sugars.
Role of Oxygen in Photosynthesis
Oxygen plays a crucial role in photosynthesis. During the light-dependent reactions, water molecules are split into oxygen, protons, and electrons. The freed oxygen is released into the atmosphere, supporting the respiration of most organisms on Earth.
Ramdon supports agricultural industries by providing insights into how optimised conditions for photosynthesis can enhance crop yields. By understanding the integral role of oxygen within plant biology, agricultural practices can be tailored to increase efficiency and productivity.
Additionally, maintaining proper levels of sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide is essential, as all these elements are interwoven within the photosynthetic processes, ultimately leading to the production of vital oxygen and glucose.
Impact of Photosynthesis on the Ecosystem and Climate

Photosynthesis plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of carbon and oxygen in the ecosystem and regulates the climate. It influences the carbon cycle, contributes oxygen to the atmosphere, and supports life on Earth.
Photosynthesis and the Carbon Cycle
Photosynthesis drives the carbon cycle by converting carbon dioxide (CO₂) into organic compounds. Plants, algae, and certain bacteria absorb CO₂ from the atmosphere during photosynthesis. This process, known as carbon fixation, reduces the concentration of greenhouse gases, helping mitigate climate change.
Photosynthesis generates carbohydrates and starches, which are essential for plant growth. The energy stored in these organic molecules supports not only plant life but also the entire food web, as herbivores and other members of the food chain depend on plants for nourishment.
Contribution to Earth’s Atmosphere and Life
Oxygenic photosynthesis releases oxygen as a byproduct, replenishing Earth’s atmosphere with this essential gas. The presence of oxygen enables aerobic respiration, which is crucial for the survival of most life forms, including humans.
The oxygen generated by photosynthesising organisms, such as plants and algae, maintains atmospheric balance. This continuous oxygen production supports not only animal life but also helps break down organic matter, cycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Overall, photosynthesis forms the foundation of life on Earth, influencing atmospheric composition, climate, and biological diversity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Oxygen plays a pivotal role in photosynthesis and contributes to various aspects of plant growth and health. Below are some common questions related to this topic.
What role does oxygen play within the photosynthetic process of plants?
Oxygen is a by-product of photosynthesis. During this process, light energy splits water molecules into oxygen, protons, and electrons. The oxygen is then released into the atmosphere, while the electrons and protons are used to produce energy-rich compounds like glucose, essential for plant biology.
In which organelle does photosynthesis take place?
Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells. These organelles contain chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for capturing light energy, which fuels the chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Why is respiration necessary for plants despite their ability to photosynthesise?
Plants need respiration to convert the energy stored in glucose into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), a usable form. Although photosynthesis produces glucose, respiration ensures that energy is available for cellular activities, growth, and maintenance of plant health.
Can you list the main products formed as a result of photosynthesis?
The primary products of photosynthesis are glucose and oxygen. Glucose serves as an energy source and a metabolic intermediate for various biosynthetic pathways. Oxygen, on the other hand, is emitted as a gas into the atmosphere, crucial for respiration in both plants and animals.
How is oxygen production linked to plant growth and health?
Oxygen production indicates that photosynthesis is occurring efficiently, which is vital for plant growth—efficient photosynthesis results in higher glucose levels, providing the energy needed for growth and development. Healthy oxygen production is often linked to overall plant health.
Why do plants exhale oxygen, and what implications does this have for the environment?
Plants release oxygen as a waste product of photosynthesis. This exhalation of oxygen is crucial for maintaining atmospheric oxygen levels, which support the respiratory needs of animals and humans. Environmental implications include the role of plants in carbon cycling and mitigating climate change.


